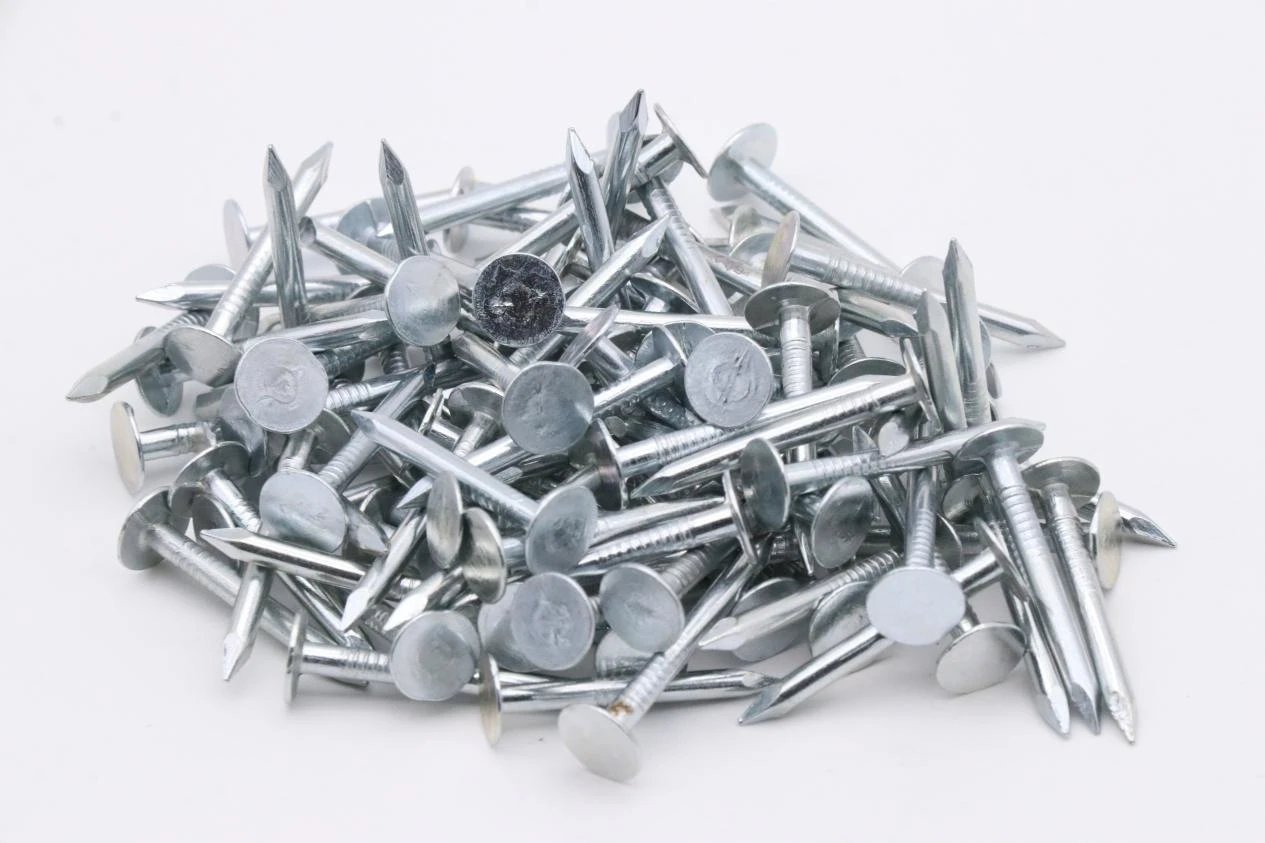
3 4 in roofing nails
Déc . 25, 2024 05:01
Understanding 3% and 4% Roofing Nails A Detailed Guide
When it comes to roofing projects, selecting the right type of nails is crucial for ensuring durability and stability. Among the different options available, roofing nails that come in 3% and 4% variations have become a topic of interest for professionals and DIY enthusiasts alike. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of these specifications and how they impact the overall roofing process.
What are Roofing Nails?
Roofing nails are specialized fasteners designed for securing roofing materials, such as shingles, tiles, and metal roofing. Their unique design, typically featuring a large flat head and a sharp point, allows for effective penetration through various roofing substrates. The size and material of these nails can vary, influencing their suitability for different roofing applications.
Understanding 3% and 4% Variations
The percentages associated with roofing nails, such as 3% and 4%, generally refer to the concentration of materials, coatings, or specific properties in the nails. In the context of roofing, these figures often relate to the tensile strength, corrosion resistance, or the ratio of specific materials used in the nail's composition.
- 3% Roofing Nails Nails categorized within this percentage typically indicate a lower concentration of certain materials, which may affect their strength and lifespan. For instance, a nail with a 3% concentration of a protective coating might not be as resistant to rust and corrosion as its 4% counterpart. These nails might be suitable for roofing in environments with moderate weather conditions where the risk of rust is lower.
- 4% Roofing Nails In contrast, nails with a 4% concentration often provide enhanced durability and corrosion resistance. This higher percentage usually means better protection against the elements, making them ideal for regions that experience high levels of moisture, severe weather, or exposure to corrosive substances. Choosing 4% nails can lead to longer-lasting roofing systems, which ultimately enhances the overall value of the property.
3 4 in roofing nails

Choosing the Right Roofing Nails
Selecting between 3% and 4% roofing nails should be based on several factors, including
1. Environmental Conditions Consider the climate of the area where the roofing will be installed. If you live in a region prone to humidity, heavy rain, or coastal salt exposure, 4% nails are likely the better choice due to their increased resistance to corrosion.
2. Roofing Material Different roofing materials may require different types of nails. For example, asphalt shingles typically require roofing nails with a large enough head to prevent water from penetrating underneath. The nail's material and coating—indicated by the percentage—will influence its performance in securing these materials.
3. Installation Technique Professional roofers often have specific preferences based on experience and project requirements. Some may prefer 4% nails for peace of mind and enhanced durability, while others might opt for the more economical 3% nails in less challenging conditions.
4. Cost Considerations Generally, the price can differ between these two types of nails. Investing in 4% nails may seem more expensive initially, but considering the long-term benefits, such as fewer repairs and replacements, can justify the cost.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the differences between 3% and 4% roofing nails is essential for making informed decisions for your roofing projects. While 3% nails may suffice in certain environments, 4% nails offer superior durability and corrosion resistance that can enhance the longevity of your roofing system. Always consider the environmental conditions, roofing materials, and cost implications when selecting the appropriate nails for your roofing needs. Investing in high-quality roofing nails today can lead to significant savings and peace of mind in the future.







 Unity
Unity Creation
Creation Challenge
Challenge Contribution
Contribution