Versatile Solutions for Strengthening Coastal Structures through Innovative Gabion Applications and Designs
Jul . 23, 2024 15:35
Gabion Walls A Sustainable Solution for Modern Infrastructure
In recent years, the use of gabion walls has gained traction in the fields of civil engineering and landscaping. Gabions, which are essentially wire mesh baskets filled with stones or other materials, provide a versatile and sustainable approach to erosion control, noise reduction, and aesthetic enhancement of various environments. This article explores the benefits, applications, and construction methods of gabion walls, underscoring their growing importance in modern infrastructure.
Understanding Gabions
The term gabion comes from the Italian word gabbione, meaning big cage. Traditionally, gabions were used in military applications, where they served as protective barriers against enemy fire. Today, they are commonly employed in civil engineering projects, landscape architecture, and environmental management. Gabion walls are constructed by placing wire cages filled with natural stone, concrete, or other materials, creating a strong and durable structure.
Benefits of Gabion Walls
One of the primary advantages of gabion walls is their sustainability. The materials used are often locally sourced, minimizing transportation emissions and supporting the local economy. Additionally, gabions allow for natural drainage, reducing the risk of water accumulation and subsequent erosion. This feature makes them particularly effective in areas prone to heavy rainfall, as water can flow through the gaps in the stones instead of pooling and causing damage.
Gabions also promote biodiversity. When deployed in landscaping, gabion walls can be integrated with vegetation, creating habitats for various species. Planting on and around gabions encourages wildlife, helping to maintain ecological balance. Furthermore, gabion walls can provide sound insulation, making them an excellent choice for installations near busy roads or industrial areas.
gabion one
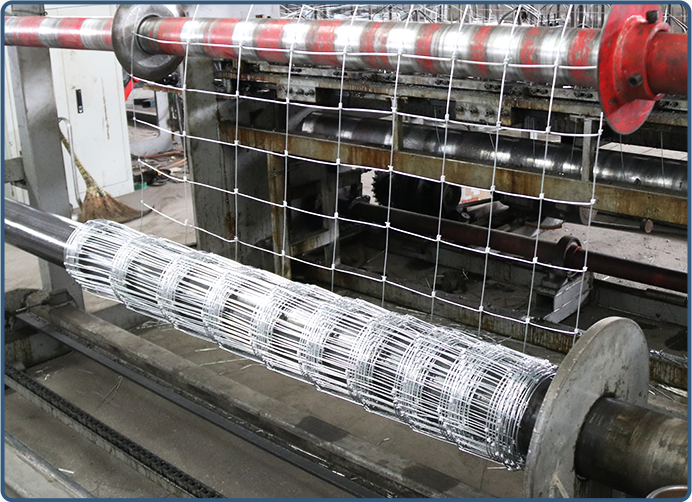
Applications of Gabion Walls
Gabion walls are used in a variety of applications, demonstrating their versatility. In civil engineering, they are often employed for slope stabilization, riverbank protection, and retaining walls. Their robust design helps prevent soil erosion and manages water runoff, which is particularly crucial in flood-prone areas. In addition to functional benefits, gabion structures can also enhance the aesthetic appeal of infrastructure projects, transforming utilitarian designs into visually pleasing features.
In landscaping, gabion walls can serve as garden boundaries, seating areas, or decorative features in parks and public spaces. Their natural stone appearance blends well with the environment, offering a rustic charm that complements nature. Designers appreciate that gabions can be customized in size and shape, allowing for creative flexibility in installation.
Construction Methods
The construction of gabion walls typically begins with preparing the site and laying a stable foundation. The wire mesh baskets are then positioned and filled with stone or other chosen materials. It is crucial to ensure that the stones are compactly packed to create a stable structure. After filling, the tops of the gabions are closed and fastened securely. Depending on the project, vegetation can be introduced to enhance the ecological benefits of the structure.
In conclusion, gabion walls represent a sustainable and effective solution for modern infrastructure challenges. Their ability to control erosion, promote biodiversity, and provide aesthetic appeal makes them an attractive option for engineers and landscape architects alike. As society continues to prioritize environmentally friendly practices, gabions will undoubtedly play a significant role in shaping resilient and visually appealing landscapes. With their multitude of benefits and broad range of applications, gabion walls are not just a functional component of infrastructure; they are a testament to the harmonious coexistence of human development and nature.







 Unity
Unity Creation
Creation Challenge
Challenge Contribution
Contribution