post for grape vines
11 月 . 04, 2024 15:20
The Art and Science of Growing Grape Vines
Grape vines, cherished for their luscious fruit and the fine wines they produce, have been cultivated for thousands of years. The process of growing grape vines is both an art and a science, combining traditional farming techniques with modern agricultural practices. Understanding the essential elements involved in cultivating grape vines can significantly enhance the quality of the grapes, leading to superior wines and bountiful harvests.
Choosing the Right Variety
The first step in grape vine cultivation is selecting the right variety for your climate and soil conditions. There are thousands of grape varieties, each with unique characteristics and growing requirements. Some popular varieties include Cabernet Sauvignon, Chardonnay, and Merlot. Local climate, soil type, and disease resistance should guide your decision. Consulting with local viticulture experts can provide valuable insights into the most suitable varieties for your region.
Site Selection and Preparation
Location is crucial for successful grape cultivation. Vines thrive in well-drained, fertile soils with plenty of sunlight. Ideally, look for a slope that allows for good air drainage and sun exposure. Before planting, prepare the site by testing the soil pH and nutrient levels. Amend the soil as needed to ensure it is conducive to vine growth. This preparation might include adding organic matter, adjusting pH, or incorporating fertilizers.
Planting Techniques
When it comes to planting grape vines, timing and technique matter. The best time to plant is usually in early spring or fall, allowing the vines to establish their roots before the heat of summer or winter frost. Space your vines appropriately—typically six to eight feet apart—to ensure ample room for growth and air circulation. Plant the vines deeply enough to promote healthy root development, while ensuring that the graft union (if applicable) is above the soil line.
Training and Pruning
post for grape vines

Grape vines require training and pruning to maximize yield and fruit quality. Training involves establishing a structure for the vine to grow, often utilizing trellises or arbors. Regular pruning is essential for maintaining healthy growth, removing dead wood, and encouraging fruitful shoots. The best time to prune is during the dormant season, usually late winter. By cutting back excess growth, you promote better air circulation and light penetration, leading to healthier grapes.
Irrigation and Nutrient Management
Proper irrigation is vital for grape vines, particularly in dry regions. Drip irrigation is often recommended to provide consistent moisture without water waste. Additionally, manage soil nutrients carefully; periodic soil testing can help determine the appropriate amounts of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium to apply.
Pest and Disease Control
Grape vines are susceptible to various pests and diseases, including powdery mildew and aphids. Implementing an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) approach can mitigate these risks. This may involve using resistant varieties, maintaining vine health through proper care, and applying organic or chemical treatments only when necessary.
Harvesting
Timing your harvest is crucial to producing quality grapes. Monitor sugar levels in the fruit, as well as acidity, to determine the optimal harvest time. Hand-harvesting is usually preferred to ensure that the grapes are picked at the right moment without damage.
In conclusion, growing grape vines is a rewarding endeavor that requires attention to detail and a passion for the craft. With the right variety, careful site preparation, and diligent vineyard management, enthusiasts can cultivate healthy, fruitful vines that contribute to the age-old tradition of winemaking. Whether you're aiming to produce exceptional wines or simply enjoy fresh grapes, the journey of growing grape vines is sure to be a fulfilling one.



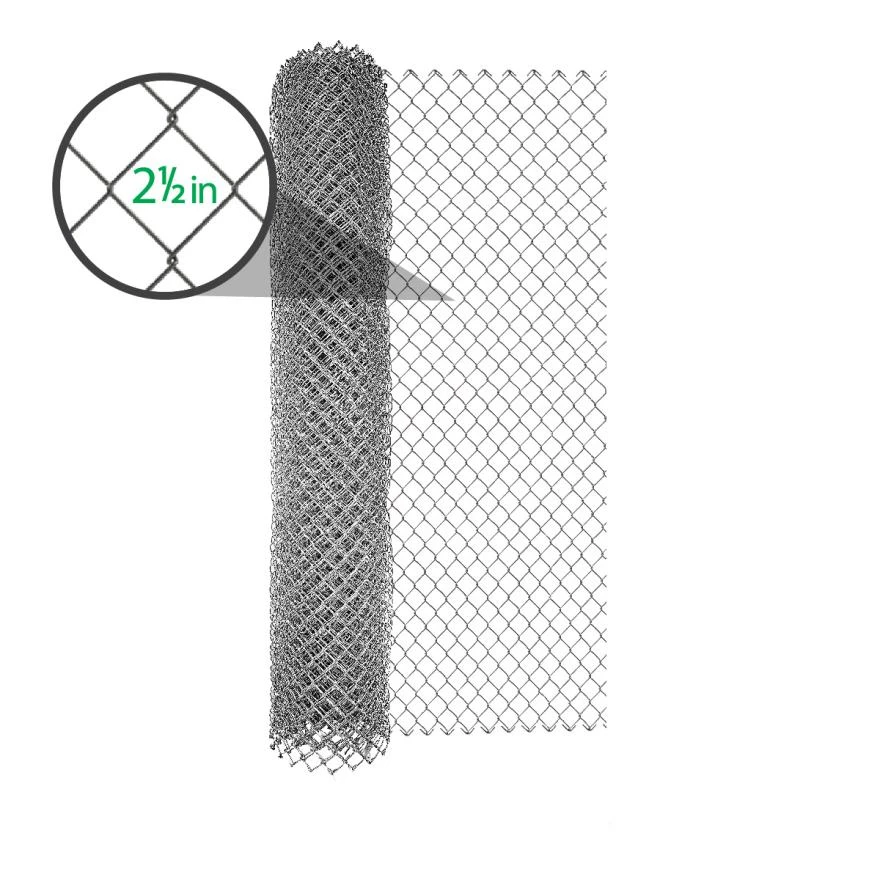



 Unity
Unity Creation
Creation Challenge
Challenge Contribution
Contribution