t pole fence
Nov . 18, 2024 18:09
The T-Pole Fence A Sustainable Solution for Modern Agriculture
As agricultural practices evolve in response to changing climates and growing populations, farmers and landowners are increasingly seeking sustainable solutions to manage their land effectively. One such solution that has garnered attention is the T-pole fence. This innovative fencing mechanism not only offers functional advantages but also embodies environmentally friendly principles conducive to modern agricultural practices.
What is a T-Pole Fence?
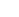
A T-pole fence consists of vertical posts that resemble the letter T set at regular intervals, creating a sturdy structure for enclosing livestock, protecting crops, or demarcating property lines. Unlike traditional fencing methods that often rely on wood or metal, T-pole fences typically utilize sustainable materials that can be sourced locally, which reduces their ecological footprint and overall costs.
The poles themselves can be constructed from various materials, including recycled plastics, metal pipes, or specially treated timber. The horizontal component of the T can be a single wire or a series of wires that can be adjusted as needed, allowing farmers to modify the height of the fence for different livestock or uses. This adaptability is one of the key benefits of the T-pole fence; it can effectively serve multiple purposes across a wide range of agricultural needs.
Advantages of Using T-Pole Fences
1. Cost-Effectiveness One of the primary reasons farmers opt for T-pole fencing is its affordability. The materials needed for construction are often cheaper than those for traditional fencing, and the installation process can be done with minimal labor, thereby reducing overall costs.
2. Durability and Longevity T-pole fences are designed to withstand various environmental conditions, including extreme weather, which often leads to the deterioration of wooden fences. When made from corrosion-resistant materials, T-pole fences can last for decades with little maintenance.
t pole fence

3. Versatility The T-pole design allows for flexibility. Farmers can easily modify the fence to accommodate different livestock sizes or make adjustments to fit seasonal needs. Whether for cattle, sheep, goats, or even as temporary fencing for rotational grazing, the T-pole fence caters to diverse requirements.
4. Minimal Environmental Impact By using sustainably sourced materials and allowing for efficient land use, T-pole fences lessen the overall ecological footprint of farming operations. They are particularly suitable for organic farming practices, where maintaining a healthy environment is essential.
5. Ease of Installation and Maintenance For many farmers, the simplicity of installing a T-pole fence is a significant advantage. Its modular design means that repairs or extensions can be made quickly, allowing farmers to react promptly to changes in their needs or conditions.
Constructing a T-Pole Fence
Building a T-pole fence involves a straightforward process. First, the layout should be determined based on the specific needs of the landowner—whether to enclose livestock, protect a garden, or create boundaries.
Next, T-poles are strategically placed approximately 10 to 12 feet apart in the ground, ensuring they are secure enough to withstand pressure from animals and environmental factors. The horizontal wire is then threaded through each T-pole, providing the necessary enclosure. This design not only enhances the structural integrity of the fence but also reduces the chances of sagging over time.
Conclusion
In an era where sustainable agricultural practices are more crucial than ever, the T-pole fence offers a practical, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly solution for landowners. From its robust construction and longevity to its adaptable nature, the T-pole fence stands out as a viable alternative to traditional fencing methods. As farming continues to adapt to modern challenges, innovative solutions like the T-pole fence will play a pivotal role in promoting sustainable agriculture, ensuring that future generations can continue to cultivate and care for the land responsibly.