Understanding Mesh - The Basics
Mesh is a material characterised by its grid-like structure, composed of interconnected strands of metal, fibre, or other flexible/ductile materials.
As a result of its unique configuration, mesh is an invaluable resource in a wide variety of fields due to its combined strength, flexibility, and permeability. From industrial and architectural applications to artistic and domestic ones, it has a wide range of applications.
At the core of mesh selection lies the decision between its two main forms: welded and woven.
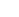
Welded mesh is created by electronically welding steel wires at their intersections, creating a strong, uniform structure with consistent spacing. Welded mesh is ideal for applications requiring rigidity due to its high stability and strength.
In contrast, woven mesh is produced by weaving metal wires over and under each other. As a result, this process is more flexible and can be customised for different weave patterns and wire diameters at the point of production, which makes it more versatile.
Also, as we always advise, weaving the wires allows for a much finer material. For example, we offer a woven mesh that has 500 wires per linear inch(which has a 0.025mm hole) whereas welded mesh rarely goes finer than 1/4″ (6mm hole). This is down to how delicate the electronic welding process can be.

Welded Mesh - An Overview
The manufacturing process of welded mesh gives it its strength and rigidity. By laying out steel wires in a grid pattern and welding them at the intersections, the mesh gains a stronger bond that enhances its structural integrity. As a result, uniform openings are created throughout the mesh, resulting in consistent and reliable strength.
The key characteristics of welded mesh include its high strength-to-weight ratio, rigidity, and minimal maintenance requirements. Despite its rigidity, welded mesh maintains its shape under pressure thanks to its strength in load-bearing applications. The welded intersections also prevent the wires from shifting, making the structure stable and durable.
Welded mesh is used in a variety of industries. The construction industry uses it to reinforce concrete in buildings and roads, providing additional strength and support. Providing a long-lasting and robust barrier, its rigidity and durability make it a popular choice for fencing. The strength and stability of welded mesh are essential in applications such as machine guards, animal enclosures, and storage racks.
Depending on your application, we offer a wide range of wire gauges, mesh sizes, and materials. Whether you need galvanised welded mesh for outdoor use or stainless steel mesh for food processing or marine environments, our products meet the highest standards. Through our expertise in mesh products, we are able to provide not just a product, but a solution that aligns with your requirements.
Woven Mesh - An Overview
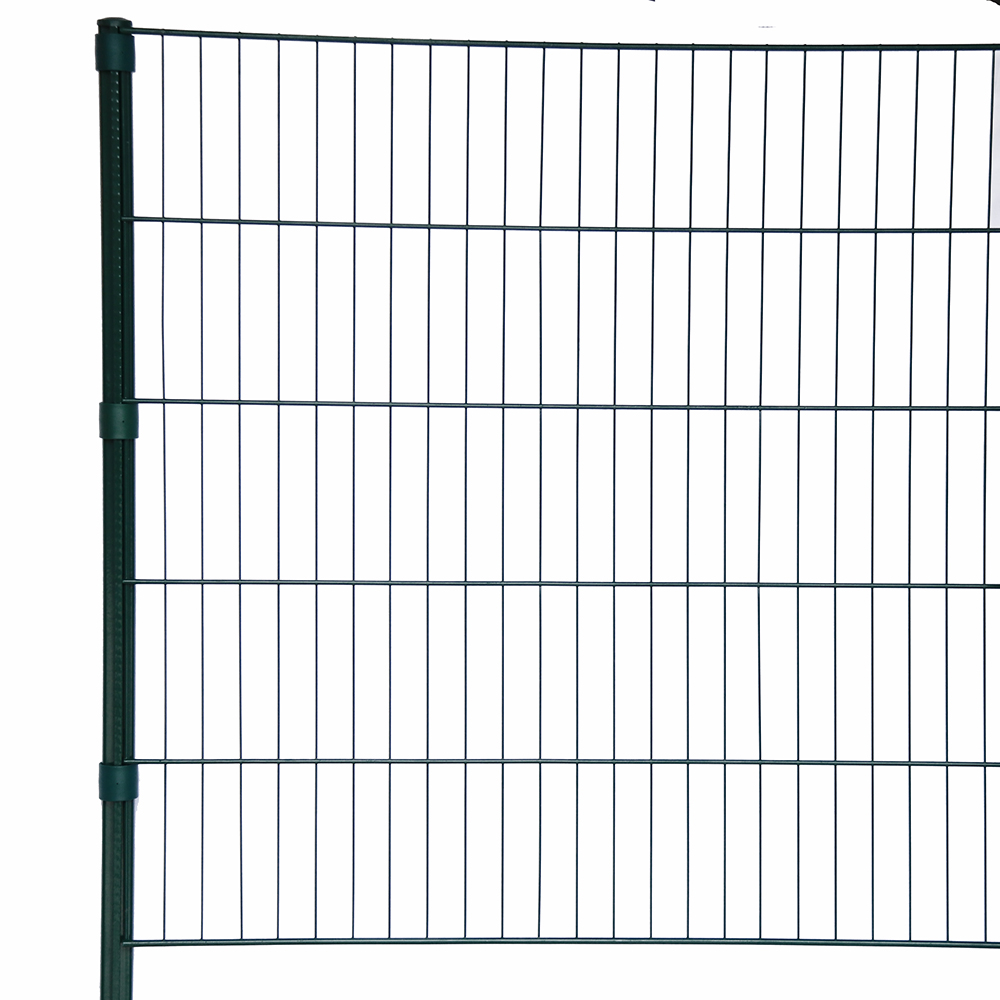
Woven mesh, often likened to the process of weaving cloth, is crafted by intricately interlacing metal wires over and under each other. As a result of this manufacturing process, a wide variety of weave patterns, wire diameters, and materials can be used, resulting in an extremely versatile and adaptable product. Mesh is characterised by its flexibility and ability to be tailored to specific applications due to the weaving process.
The standout features of woven mesh include its flexibility and adaptability. Unlike welded mesh, which is rigid, woven mesh can conform to various shapes and absorb impact without breaking. As mentioned previously, it can be as fine as fabric.
The material is particularly suitable for bending and curving applications due to this quality. Moreover, the weave pattern can be adjusted during the looming process to control the mesh’s permeability and strength, making it an ideal choice for fine filtration and screening.
Numerous industries use woven mesh. Filtration uses sieving and straining to separate liquids and solids. In screen printing, where consistency and fine detail are crucial, woven mesh is ideal. For decorative facades, woven mesh offers both aesthetic appeal and functional benefits, such as light diffusion and ventilation.
Stainless steel meshes are corrosion-resistant, while brass meshes are considered aesthetically pleasing. We offer woven meshes in different weave patterns, from plain weaves to twills and Dutch weaves, each offering unique characteristics. To meet the diverse needs of our customers, our woven mesh products embody quality and versatility, whether they’re used in industrial filtration, artistic installations, or architectural design.
Welded Mesh
Comparative Analysis
Several factors come into play when comparing welded and woven mesh: strength and durability, flexibility and adaptability, applications, and maintenance.
Strength and Durability: Strong and rigid, welded mesh is made up of intersecting wires that are firmly welded together. As a result, it is ideal for applications requiring structural support, such as construction and fencing. Despite its flexibility, woven mesh excels in tensile strength, making it resistant to impact and suitable for dynamic applications despite not being as rigid.
Flexibility and Adaptability: Due to its inherent flexibility, woven mesh can be used in applications that require bending or shaping, such as curved filters and decorative architectural elements. Since welded mesh is rigid, it provides a stable, uniform structure but is less adaptable.
Applications and Suitability: Welded mesh or woven mesh depends largely on the intended application. In security fencing, animal enclosures, and concrete reinforcement, welded mesh is preferred when a strong, fixed shape is needed. With its flexibility and varied weave patterns, woven mesh is ideal for filtration systems, screen printing, and decorative applications.
Maintenance and Longevity: Both types of mesh offer good longevity, but their maintenance needs differ. As welded mesh is more rigid and stable, it generally requires less maintenance once it has been installed. The material is less prone to shifting or deforming under load, making it a reliable long-term structural solution. Despite its durability, woven mesh may require more attention in applications where it is subject to constant movement or flexing. Nevertheless, its ability to withstand impact without breaking can extend its lifespan in dynamic environments.
The choice between welded and woven mesh should be guided by the specific requirements of the project. Woven mesh provides flexibility and adaptability for dynamic and decorative applications while welded mesh provides strength and rigidity for static, load-bearing applications. Depending on the environment and application, both types feature durability and longevity.

Choosing the Right Mesh for Your Needs
When choosing mesh for your project, you must consider several key factors, each playing an important role in ensuring that the mesh not only meets but enhances the effectiveness of your application.
Purpose: Considering how the mesh will be used is the first and foremost consideration. A welded mesh is usually the best option for structural purposes or applications requiring rigidity and load-bearing capacity, such as in construction reinforcement or security fencing. Durability and strength are ensured by its stable, uniform structure. Due to its malleable nature and variety of weave patterns, woven mesh is more suitable for applications that require flexibility and adaptability, such as filtration systems, screen printing, or architectural design.
Environment: The environment in which the mesh will be used greatly influences the choice. Stainless steel and galvanised steel are ideal corrosion-resistant materials for outdoor applications or environments with high moisture or corrosive elements. Chemical or wet environments benefit from woven meshes in these materials, while physically demanding environments benefit from welded meshes for their structural integrity.
Budget: Budget constraints also play an important role in decision-making. For larger, more structural applications, welded mesh is usually more cost-effective, while woven mesh is more expensive, particularly when it comes to finer, more intricate weaves or specialised materials.
Another often overlooked factor is how you would like the edges to be. We recently wrote a detailed blog article discussing this.
Consider consulting with experts who have experience and knowledge of various applications when making an informed decision. Additionally, sample testing in your specific environment can ensure the mesh meets your needs.